The fungus is a type of mushroom-type ‘bug’ which has many varieties and can live in varied places, one of such types of fungus is the yeast.
You may have come across the word “yeast” during the process of making bread or any other type of baked goods, where it is used to raise the dough. But, our interest in this article is the types of yeasts which cause diseases in humans.
In this article, the yeast we will discuss in depth is a type of yeast called “candida” or more specifically candida albicans.
However, there are other types of candida, like candida glabrata and candida tropicalis.
These yeasts, mainly the candida albicans can occur naturally in the body without causing any harm or disrupting our body’s natural balance. They thrive in warm, dark and moist places. Therefore, they can occur or grow in the skin, vagina, digestive system, mouth etc.
Also, in this article, we will get to know how yeast can cause an infection and all the details about it. Most importantly, we will be concluding the article addressing the question ‘Can you Die from a Yeast Infection?’
Let’s start exploring by defining yeast infections better.
Tip: Is Warts or Molds on the skin are due to fungus or viral infections? We covered that before providing some preventative tips for warts.
What is a Yeast Infection?
When yeast grows or divides out of proportion disrupting the delicate balance of the body, it is called yeast infection or “Candidiasis” or “Moniliasis”.
Under normal conditions, our immune system is capable of controlling or inhibiting the overgrowth of this yeast. Still, certain conditions trigger a change in the environment that these yeasts are found, causing them to divide out of proportion.
Yeast infection can occur in the mouth, oesophagus, under the armpit, vagina, penis and on the skin.
Tip: Did you know that recurrent episodes of thrush can be an early warning sign of diabetes in men, women and children.
Which Conditions Promote Yeast Infections?
The conditions that can trigger this change in the environment causing yeast infections are below.
- A weakened immune system such as when a person is sick, for e.g. a person with HIV/AIDS, cancer, diabetes
or leukemia etc.
- When antibiotics are abused or normally such as when you take antibiotics which alter the bacterial flora in your body.
- When the area the yeast stays is dark and also exposed to the warm temperature and moisture, it creates a favourable environment for the yeast.
- Constant wear of tight-fitted undergarments.
- Use of soaps, body cream, perfume or deodorant that your body reacts to by manifesting as irritation.

Tip: If you have diabetes, high blood pressure or mental health conditions, then you much focus on managing those conditions well to avoid reoccurring yeast infections.
Common Yeast Infections in Men, Women, Children and The Aged
It should be noted that yeast infection does not affect only one group of people, they are common in both women, men, the aged and as well as in children or toddlers. They also can occur at any point in our lives.
Here are the common types of yeast infections.
- Oral yeast infections (commonly known as a ‘thrush’)
- Vaginal yeast infections
- Penile yeast infections
- Diaper yeast infections
- Esophageal yeast infections
1. Oral Yeast Infections
Oral yeast infection also is known as Thrush, or oropharyngeal yeast infection is a yeast infection of the mouth and throat.
Earlier I mentioned that yeast can normally live in the mouth or throat, so when certain conditions trigger their overgrowth, it leads to an infection.
The oral thrush appears as whitish or yellowish patches on the inner surface of the cheeks and on the tongue.

Oral yeast infections are common in babies, toddlers and adults.
Oral Yeast Infection in Babies and Toddlers
Like in adults, don’t forget that yeast also lives naturally in the mouth of babies too!
In babies, most people mistake oral yeast infection for milk or formula because of the white patch or blemishes on the inner cheeks, tongue and mouth.
They get oral yeast infections if some conditions trigger it or they may contract it from their mothers during breastfeeding, delivery or pregnancy.

Oral yeast infection can lead to the baby having difficulty and pain in swallowing, ultimately this can lead to malnutrition.
Oral Yeast Infection in Adults
Oral yeast infection can occur at any age, though you can say it can be common to a specific age group, for, e.g. in the older adults maybe it is due to their weakened immune system.
It can occur in adults of younger age, especially if their immune system is compromised etc.
Once experienced, it can lead to serious medical conditions if your immune system is weakened causing it to spread to other body organs and parts.
Note that the same kind of yeast that lives in the mouth is the same kind that can live anywhere in the body, once spread.
Risk Factors That Predisposes You To an Oral Yeast Infection – The Oral Thrush
Here are the things that can cause one to be at risk of getting thrush.
- Wearing dentures
- Compromised or weakened immune system like people with HIV/AIDS
- Unhealthy lifestyle, like smoking
- Unhealthy eating habits
- Newborn babies
- Chemotherapy or other cancer treatment mechanisms
- Through breastfeeding, delivery when the mother is infected etc.
- Taking drugs such as antibiotics, immunosuppressant and steroids

How To Prevention an Oral Yeast Infection (Thrush)?
Thrush can be prevented or avoided through these methods.
- Brush your teeth with a toothpaste product that contains fluoride and also scrap your tongue twice daily
- Remove your dentures before going to sleep every day and follow the necessary cleaning method as directed by your Dentist
- Don’t abuse antibiotics, only take them if directed by your doctor
- If as a new mother, you have a yeast infection in your breast or anywhere, or your baby has a yeast infection, it can be contagious between two of you.
- If you suffer from dry mouth, do see your doctor for treatment.
Tip: As our Knee Pillow Guide indicates knee pillows can make a massive difference in helping you sleep comfortably. The Calming Comfort and ComfiLife are currently considered leading knee pillows.
2. Vaginal Yeast Infections
This is the most common type of yeast infection, and it is common in women. It is the overgrowth of yeast or candida in the vagina leading to a condition known as the vaginal yeast infection or candidal vulvovaginitis or vaginal thrush.
The vagina has a rich microbial flora that is balanced and kept in check by the body. So, it’s normal for yeast or bacteria to be found in the vagina. And, that is why it’s advised to stop douching or using scented or antiseptic soap to wash the vagina as this can disrupt the delicate balance of the vagina leading to irritation, yeast infections or other types of infections.

As stated in the articles “titled vaginal yeast infection fact sheet” and “diagnosis of vaginitis” by womenhealth.gov and Egan M. E. et al., it was found that about 75% of women at some point in their lives have at least one vaginal yeast infection. In contrast, nearly half of all women have two infections. About 5% of the women have at least 3 infections in a year.
What Are The Risk Factors To Get Vaginal Yeast Infections?
The following can cause you to be predisposed to a vaginal yeast infection, or recurrent infections.
- Pregnancy – some hormones like oestrogen, which women secrets can increase in the level.
- Lifestyle habits like smoking or eating sugary foods
- Unchecked diabetes
- Use of soaps or toiletries products that irritates the vagina
- Oral sex etc.
How Do I Prevent a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
Here are some tips about how you could prevent vaginal candida infection.
- Avoid the use of toiletries or products that irritates the vagina.
- Avoid tight-fitting underwear
- Eat healthily
- Avoid indiscriminate use of antibiotics
- Since yeasts thrive on the warm and moist environments, avoid wearing wet underwear or swimsuit for a prolonged period
Tip: Some essential oils can help you prevent yeast infections.
3. Penile Yeast Infections – Yeast Infections of The Penis
Penile yeast infection, candidal balanitis or balanitis thrush is an overgrowth of yeast in the penis or in the genital region of men. It is uncommon, often yeast infection is thought to be found only in females, but recently its existence in the male genital area has been discovered.
Risk Factors For a Penile Yeast Infection
● This infection is transmitted in males through unprotected sexual intercourse between a male and a female that is already infected with candidal vaginalis.
● Men that are not circumcised stand a higher chance of contracting it.
● Yeast infection thrives easily in a warm, moist and dark environments, so poor hygiene exhibited by the male can also serve as a risk factor.
● Prolonged use of antibiotics, especially in a diabetic or obese male, can increase the risk of having this infection.
● Impaired immune systems due to the treatment of cancer can cause one to easily contract this yeast infection.

Tip: Healthy active lifestyle is essential to overall boost your immunity. If you have diabetes, follow a care plan to manage it. If you are less mobile, use a mobility aid to help you keep active.
How to Prevent a Penile Yeast Infection?
In order to prevent a yeast infection, it is advisable to do the following.
● Avoid having sex with a partner that has this infection or having sex with anyone when you have this infection.
● Practice good hygiene; always keep the genital region clean and dry.
● Avoid tight-fitting briefs or underwears.
4. Diaper Yeast Infections (Diaper Rash)
This is a type of yeast infection common in infants, toddlers or elderly who are or because they wear diapers.
The main cause of this yeast infection is as a result of prolonged wear of wet or soiled diaper, that’s why the prevalence of diaper yeast infection drops as the infant or toddler grows and starts wearing cotton pants or if they were potty trained earlier.
In babies, the diaper yeast infection can also be caused by contact with an infected mother or if the infant has a yeast infection in another area of the body.
A diaper yeast infection often appears as rashes on the baby’s buttocks, but that is not a basis for diagnosis as some rashes in that area are not necessarily yeast infection. One thing that differentiates diaper yeast infection from other types of diaper rash is the presence of red bumps or pustules.
Risk Factors For Diaper Yeast Infections
Here are the risk factors.
- Infant’s who wear diapers, and when the wet wipers contact longer on to the body.
- Misuse of antibiotics.
- Presence of yeast infection in other areas of the infant’s body.
- If the mother has a yeast infection, this can be passed to the infant through breastfeeding or contact.

How To Prevent a Diaper Yeast Infection?
Here are some guidelines anyone with a ‘high-risk’ should follow to prevent diaper yeast infections.
● Remember that yeast love moist and warm environments so, therefore, change diapers frequently and sometimes delay wearing his/her diapers to allow the buttocks air.
● Wash the infant’s pacifiers with hot water and also replace the pacifiers when it is old
● Avoid the misuse of antibiotics as this can kill the beneficial bacteria leading to the overgrowth of yeast.
● Wash the infant’s bottle nipple with hot water and also replace old ones.
● Yeast infections are not restricted to the diaper area, so check or if there is a yeast infection elsewhere because there is a likelihood that it could be contagious.
5. Esophageal Yeast Infection
Esophageal yeast infection, Candida Esophagitis or esophageal thrush is the overgrowth of yeast in the oesophagus.
The esophagus is a tube or canal that connects your mouth to your stomach, and it is the second most susceptible part of the gastrointestinal tract that is more prone to yeast infection.
Just like other types of yeast infection, esophageal yeast infection is common among people with an immunocompromised system, people who have HIV/Aids, cancer and leukemia etc. or people who abuse antibiotics.
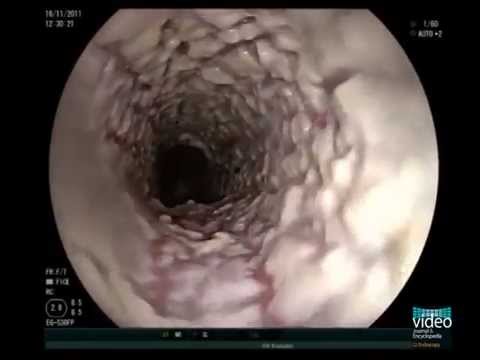
Risk Factors For Esophageal Yeast Infection
It is the same for other types of yeast infection, for, e.g. smoking, weak immune system etc. (just check the risk factors for other yeast infections noted above)
Prevention of Esophageal Yeast Infection
It can be prevented the same way the previous yeast infections, as discussed above.
Signs and Symptoms of Yeast Infections
In this section, we will look at the signs and symptoms of specific types of yeast infection; though most of these signs and symptoms overlap are similar.
Signs and Symptoms of Oral Yeast Thrush
The thrush symptoms are here.
● White or yellow inner cheek patches
● Redness inside the mouth, inner cheeks and throat.
● Loss of taste or bad taste on the mouth.
● Dry cracks on the outside of the mouth.
● Painful sensation in the mouth, especially when swallowing and chewing.
● Bleeding
Signs and Symptoms of Vaginal Yeast Infection
Here are the vaginal thrush symptoms.
- Irritation and itching of the vagina.
- Thick discharge from the vagina, which is most likely odourless.
- Odor or unpleasant smell from the vagina.
- Pain during menstruation, urination and sexual intercourse.
Signs and Symptoms of Penile Yeast Infection
● Irritation or itchiness on the tip of the penis, or the skin around the male genital area.
● There can be inflammation of the foreskin of the penis for those who are uncircumsized.
● A whitish discharge which is odorless.
● Discomfort during sexual intercourse.
● A red rash with pimple-like bumps on the penis or around the genital area.
● White patches on the genital area.
Note, that some infections mimic a penile yeast infection, so before any treatment, see your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Signs and Symptoms of Diaper Yeast Infection
Here are diaper-related infection signs.
- The appearance of red rashes in the groin area, buttocks and in between skin folds (i.e. that is between the thigh and buttocks).
- With red pimple-like bumps on your private areas.
Signs and Symptoms of Esophageal Yeast Infection
Let’s look at the oesophageal yeast infection symptoms.
● Affected persons lose weight due to poor nutrition.
● Pain when swallowing.
● Whitish lesions on the lining of the esophagus, which can be seen through a medical procedure using an endoscope (upper GI endoscopy).
● Frequent dry mouth.
● Pain in the chest or chest angina.
● Nausea and vomiting etc.
● Symptoms of reflux.
Tip: Remember, stress can cause physical pain in your body too.
When Should You Call Your Doctor To Diagnose and Confirm a Yeast Infection?
Most times the signs and symptoms of yeast infections are often similar to other types of infections. Therefore, it is always recommended visiting the doctor for proper diagnosis.
Other reasons why you may want to see your doctor is if it is your first time having any infection if over-the-counter drugs or home remedies didn’t relieve or cure the yeast infection.

If you have a compromised immune system, e.g. you have cancer, leukemia or any other disease.
If the doctor is confident if you have a yeast infection once examined for the signs of the yeast infection, he/she will start anti-fungal or anti-yeast treatment without a laboratory test.
If further confirmation required for the doctor to initiate treatment, then a laboratory test will be requested.
In the diagnosis of a specific type of yeast infections, the doctor will collect a pathology sample and sent it to the laboratory for examination under a microscope or cultured to determine if it is a yeast infection before treatment starts.
The following procedures might be involved in collecting a sample.
- The inside of the mouth, the diaper area, the discharge from the genital area (for the vaginal and penile yeast infection) – sample of any discharge swatted with a cotton bud or any other device.
- The inside of the esophagus – using endoscopy procedure a sample may be collected to differentiate thrush from oesophageal cancer
Treatments for Yeast Infections
Sometimes healthy adults take antifungal medications to treat yeast infections. These medications are even given to healthy infants before seeking medical advice.
In most of the cases, the above approach works okay unless medication fails after some days, a week or the symptoms become worse by accompanied by fever or chills.
As such, ‘self-diagnosing’ can ‘go wrong’ easily, and that’s why we encourage you to see your doctor.
Tip: Do not use hydrogen peroxide on fungus infections.
People with a compromised immune system must see the doctor at the first signs or symptoms of such yeast infections for proper diagnosis because this can lead to disastrous complications and sometimes even death.
Over-The-Counter (OTC) Medicine for Yeast Infection
Here are some OTC drugs you can get without a prescription from a drugstore in most of the countries. In some states, a doctor should prescribe them for you to collect them from a pharmacy.
For the general treatment of yeast infection, some of the common OTC antifungal medications which can be available as tablets, creams.
They are:
- fluconazole,
- clotrimazole,
- imidazole,
- miconazole and
- terconazole etc.
Home Remedies for Yeast Infections
The efficacy of home remedies in the treatment of yeast infections has not been proven. There are no enough research studies been done on them, but some field of thought swears by it.
Again, it is essential that you seek the advice of your doctor before trying them.
Here are some of the home remedies for the treatment of yeast infections.
- Tea tree oil
- Oil of Oregano
- Garlic
- Apple cider vinegar
- Coconut oil
- Greek yogurt
Along with these treatments, it is advised for you to practice general body hygiene so as to avoid recurrent yeast infections and their complications.

In the treatment of penile yeast infection, if the man is uncircumcised and the infection responds poorly to antifungal medications, some doctors can recommend circumcision.
Tip: It is believed that Chinen Salt can prevent skin infections.
What Happens If Yeast Infections are Left Untreated? Complications of Yeast Infections
Normally in healthy adults or infants, yeast infections go away after a few days, especially when the causes of that yeast infection are addressed. However, if a yeast infection is left untreated for a while, it can lead to serious complications.
- Invasive yeast infection
- Skin infections and skin disorders
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Gastrointestinal tract (GIT) problems
- Lowered immune system
Tip: Did you know Cefaly can help you manage migraine headaches better?
Can Yeast Infections Enter The Bloodstream?
Yes, a yeast infection can, and it is through a condition known as invasive yeast condition.
This condition is when yeast infection enters the blood, heart, spleen, brain etc.
In the case of yeast entering the bloodstream, this condition is known as candidemia.
People who are hospitalized are more predisposed to get candidemia as they are likely to receive blood donations or intravenous fluid which is via a catheter that maybe was left for a prolonged period. Such infection can be also gotten through health care providers hands since they care for many people and in the process may get yeast on their hands.
Can Yeast Infections Spread? Is Yeast Infections Contagious?
Most yeast infections don’t spread, but in some situations, they can spread.
For example, in the case of an affected mother to her child or vice versa or from male to female (rare), especially if the victim has an immunocompromised system.
In some cases, a yeast infection can spread to other body parts of the same individual.
[et_bloom_locked optin_id=optin_3][/et_bloom_locked]
Common Questions and Answers About Yeast Infection
Question: Can Yeast Infections Make You Tired?
Answer:
For healthy people, rarely, unless it was left untreated for a long time leading to complications. However, people with immunocompromised systems can experience fatigue or tiredness.
Question: Can You Get Yeast Infections From Stress?
Answer:
When our body is subjected to severe or prolonged stress, it will lead to a lowered or altered immune system, which may lead to yeast overgrowth (yeast infection).
There are scientific studies, though not yet proven, that there is a relationship between stress and vaginal yeast infection.
Question: Can You Die From a Yeast Infection?
Answer: No, unless in severe cases where the infection enters the bloodstream of an immunocompromised patient, which is rare.








0 Comments