This Guide to Help You Choose Lateral Supports for Wheelchairs to Stop Sideway Leaning, Reduce Pain and Prevent Pressure Sores will highlight the importance of body supports if you use a wheelchair. It also provides some valuable tips on identifying the best lateral support for your personal needs.
When observing someone’s sitting posture, one can ask “what is the body doing that it should or shouldn’t be doing?” When a patient sits in a position for a long period, the body begins to shift into abnormal postures in an attempt to gain stability, ease pain and pressure.
Trunk Supports, also known as Body Supports helps in stabilizing the patient while improving his/her posture.
In choosing the best wheelchair lateral trunk support for a user according to his needs and diagnosis, the progression of spinal injury and pressure sores can be prevented or even corrected, and this has a lot to do with pressure distribution and comfort.
Before digging into Trunk Supports, let’s define what Trunk is first.
What is the Trunk?
The trunk consists of three things – the thorax, abdomen and pelvis, in that order from top to bottom.
In other words, the trunk is the centerline of the body, supporting the head and keeping the body in an upright position.
The thorax, abdomen and pelvis are grouped into two enclosures – thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity, surrounded by bony and muscular walls and separated by a muscular diaphragm.
1. Thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity begins from the clavicle and first rib down to the muscular diaphragm. The ribs, thoracic vertebrae and intercostal muscles in between form its walls.
2. Abdominopelvic cavity
The abdominopelvic cavity begins from the diaphragm as the roof and the muscular pelvic the floor. The lumbar vertebrae with muscles on either side of it and the abdominal muscles form its walls. A bowl formed by the sacrum, two innominate bones with a muscular floor makes up the pelvic part of the cavity.
The trunk does a number of things including:
- Helping the lungs in breathing, through ventilating
- Protecting the organs of the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity.
- Reducing pressure on the back (spine) when doing activities like lifting loads.
Most movements of the trunk are performed by large muscles – the deep muscles of the back and the abdominal muscles.
Stability of the trunk is supported by its walls and boundaries noted above. The maintenance of that stability is important for your health and wellbeing.
Lack of Trunk Stability and Its Effects
For self-propelling users of a manual wheelchair, it may prove more labour-intensive without enough trunk stability.
Lack of trunk stability results in quite problems.
- Difficulty in holding the upper body upright and chest collapsing.
- Neck pain, shoulders moving forward, lack of head alignment.
- Stiffness in ankles or calves, causing feet to fall off footplates.
- User working extra hard to keep trunk positioned against the backrest of the wheelchair, as well as the fall risk.
- User may slide in the chair and go into posterior pelvic tilt.
- User’s leg may be unable to stay together.
- User experiencing fatigue as a result of the strain of reaching for the joystick by the side (for power wheelchair users)
- User experiencing fatigue when doing activities that require more motions, such as traveling and playing sports.
Here are some body exercises that wheelchair users can perform to strengthen and stabilize their trunks.

Tip: Did you know that a Knee Pillow could provide you with postural stability while you sleep?
What is a Side (or Lateral) Trunk Support for Wheelchair?
Trunk stabilizers also called laterals, lateral thoracic support, lateral support, or wheelchair lateral trunk support, are square/rectangular/custom shaped devices attached to the back post of the wheelchair. It is often used in pairs, one resting on each side of the user’s trunk to increase the balance and stability while providing comfort.
Wheelchair lateral trunk supports come in different padding shapes, sizes and densities depending on the style and the manufacturer.
Tip: You may find this How to Choose a Cushion for Wheelchair Guide useful too.
Types of Wheelchair Side (or Lateral) Trunk Supports
Lateral trunk supports can be stylized and made into planar or contoured shapes. The padding style has to be chosen with hardware that suits the user’s needs and care.
1. Padding
-
Broad Padding
This padding type enables long trunk support, and its contour helps in effectively reducing pressure on the user’s trunk.
-
Narrow straight Padding
This type enables free forward and backward movement for flexible, functional activities and transfers.
-
Narrow curved Padding
These paddings provide the contour increases spinal extension and comfort through anterior support.
2. Hardware
-
Standard Swing-Away
This vertical pivot adjustment allows width and depth adjustment.
-
Axial Swing-Away
This rotational system provided by axial technology enables width, depth and multiple angles adjustment.
-
Fixed
In this case, only the width and depth are adjustable.
-
Cane mount
This is easily mounted on the wheelchair’s cane.
Lateral trunk supports can be ordered or purchased directly from manufacturers or various aftermarket sources. Models can also be ordered by choosing hardware (Swing-Away for example) with a lateral (planar or contoured) that will allow the user to easily get in and out of the wheelchair.
Lateral supports are helpful in preventing abnormal posture tones. If a wheelchair user is with an unnatural posture, those laterals still can help with providing comfort and preventing pressure ulcers.
Before further due, let’s identify what abnormal postures are and what are unnatural tones.
Tip: Rooke vascular boots could help you prevent pressure ulcers in the legs.
Abnormal Posture and Tones
What is an Abnormal Posture?
Structural deformity of the spine or back pain often leads to abnormal postures. Abnormal posture is prolonged deviations from the natural curvature of the spine.
Some of the common abnormal postures are below.
-
Posterior Pelvic Tilt (Kyphosis)
This is characterized by an excessive forward curve of the upper back region and posterior pelvic tilt.
It causes the spine to hunch over and appears as a hunchback. A wheelchair user suffering from kyphosis may experience stiffness, back pain and develop sacral sores.

-
Anterior Pelvic Tilt (Lordosis)
The normal spinal curvature looks ‘S’ shaped, but when it is exaggerated, it causes discomfort, back pain and affects mobility.
The spine curves in at the neck and lower back region, and the patient appears to be tilting the head forward while sticking out the stomach and buttocks.
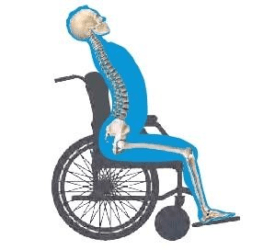
Lordosis
Tip: Here’s our Guide to Mobility and Daily Living Aid Options.
-
Pelvic Obliquity (Scoliosis)
This is the sideways curve of the spine as one pelvis tilts higher than the other. Pelvic rotation or twist comes as scoliosis progresses or becomes worse.
Scoliosis also sometimes causes other complications such as lung and heart damage (caused by rib cage pressing against the lungs and heart), back pain and difficulty breathing.
-
Pelvic Rotation
In pelvic rotation, one side of the pelvis is rotated more forward than the other, the thoracic spine follows in the same direction with one side turned more forward than the other.
What is an Abnormal Tone?
In a relaxed patient, a healthcare professional assesses the involuntary muscle tension by flexing and extending parts of the body. This involuntary muscle tension is known as muscle tone. Depending on the patient, the muscle tone may be high (hypertonic), normal, or low (hypotonic).
In dealing with low tone or high tone, lateral trunk supports can be used for stability and function by providing the optimal upright posture.
It’s is important to understand that wheelchair users are with an increased risk for pressure ulcers and injuries. The side supports can help in such pressure sores as well.
Before going into detail on how the wheelchair letterals can help to prevent pressure sores, let’s understand pressure sores better.
Pressure Ulcer/sores
A pressure ulcer is an injury caused by pressure and/ or shear force, which breaks down the skin and underlying tissues. Bony prominences are bones close to the skin surface, and they are areas under the most pressures. The bony prominences are at greatest risk of developing a pressure ulcer.
Deep tissue pressure ulcers are characterized by purple, maroon or non-blanchable deep red discoloration on the skin, even though skin appears intact.
A number of factors increase the risk of developing pressure ulcers.
- Limited movement
- Nerve damage (reduces the feeling of pain and pressure)
- Thinking and reasoning impairment
- Poor health and blood circulation
- Poor nutrition
- Unmanaged incontinence.
Lateral trunk supports and backrest when placed properly, provides strength and support to the trunk. They help the user to sit upright and balanced, which improves pressure distribution and relieves pain and pressure on pressure ulcers.
Tip: Here’s our Guide to Pressure Ulcer Prevention Products for Elderly and Bed-ridden People.
Benefits of a Side (or Lateral) Trunk Support for a Wheelchair Users
Here they are.
-
Balance and trunk stability
Lateral trunk supports are used to increase the user’s trunk stability and balance while sitting on the wheelchair.
-
Accommodating and correcting posture anomalies
Fixed/Non-Reducible Postures
When a user’s postural anomaly is determined to be fixed, that is the skeleton doesn’t move from a particular posture, lateral trunk support help provide the stability and support the user needs throughout the day.
In addition, they allow correct pressure distribution for the user when the trunk supports are properly positioned to do so.
Flexible/Reducible Posture
In the same way, if the posture anomaly is determined to be flexible and the skeleton still moves, lateral trunk supports with the proper contouring are selected to correct the ‘defect’ and prevent the condition from worsening and becoming fixed.
-
Prevents leaning
When a user has decreased trunk strength and stability and is unable to maintain posture, lateral trunk supports help to keep the user in position and prevent sideways leaning.
-
Reduce pain and pressure
By prolonged sitting, the user may begin to feel pain or skin breakdown at the Apex of the curvature due to pressure. Wheelchair trunk supports significantly decrease the pressure point on the Apex of the curvature that would otherwise cause the user pain.
-
Upright position
When a user cannot maintain an upright neutral sitting position even when the trunk is placed properly, then the lateral trunk supports can be placed on each side of the trunk opposite each other. This will give the user the needed external support to hold his position.
Importance of Lateral Body Support Placement and Body Contact
For a trunk stabilizer to work well, surface contact with the trunk is important else there will be no support.
- If the laterals are placed too high, they may press on the armpit and restrict shoulder and arm movement, cause soft tissue pain or even damage to the brachial plexus.
- If the laterals are placed too low, there is little or no support, and trunk may lean over the top of the wheelchair trunk supports.
- When the lateral trunk supports are placed too tight against the trunk, the user may have breathing problem and pains.
When the abnormal tone is asymmetric, using trunk support in addition of lateral upper leg support placed at the hip, creates a three-point system of support, which results in an upright posture and optimal pressure distribution.
This arrangement reduces flexible spine curvature as well as support the trunk.
Benefits of Lateral Wheelchair Supports in Managing Pain and Pressure Ulcers
- Pressure redistribution contours in trunk support to increase the surface area contact with the user, reducing centralized pressure and improving pressure distribution.
- Laterals provide proper trunk alignment. This ensures reduced fatigue in sitting, increased pressure distribution, improved respiration and swallowing.
- Trunk supports prevent progression of trunk deformities (such as scoliosis) due to weakness in the trunk, and relieves the trunk of pressure injuries and pain.
Tip: Want some support and confidence to get into your shower? Try this Carousel Sliding Transfer Bench with Swivel Seat.

Who Should Consider a Wheelchair Lateral Trunk Support?
There are a number of people who will need to consider the use of wheelchair lateral trunk supports, but there are justifications as to who actually qualify for them. Some of them are as follows.
- Patients with decreased strength who have difficulties with maintaining stability and balance, which exhibit poor motor control, poor endurance, abnormal tones and postures, and others.
- Patients in danger of pressure injuries to vertebrae which may be due to illness or prolonged sitting.
- Patients with a flexible spinal deformity which can be corrected.
- Patients with a fixed spinal deformity which progression can be slowed or prevented.
- Patients with pressure ulcer who need more pressure distribution.
- Patients leaning to one side in an attempt to alleviate pain or pressure.
Tip: Roho Cushions and Star Cushions are both considered good wheelchair cushions, but without limitations, as noted in linked articles.
The Downside of Wheelchair Lateral Supports
If you consider lateral body supports, then it’s worth knowing that like with anything there are cons of them too.
- The hardware swing away release may get stubborn when the pad is under pressure.
- There is no adjustment for angling the padding in or out; hence it is not possible to realize even contact of the body against the entire pad.
- Mounting the backrest in proper position may not be easy.
- If the user decides to change its position the wheelchair trunk lateral may no longer be correctly aligned.
- If the lateral supports are placed too low, then there may be no support, and it becomes ineffective.
- If lateral supports are set too high, they may affect the armpit and lead to other problems such as bronchial plexus injury and restricting movement of the arm and shoulder.
- The laterals add a complex look to the overall appearance of the wheelchair.
Tips for Choosing the Best Wheelchair Lateral Body and Trunk Supports
There are two main things to consider when choosing a wheelchair lateral trunk support; pad and hardware.
1. Pad
In selecting a pad, there are things to consider, shape, size and moldability.
Moldability
Considering that the human body is not flat, a moldable pad will allow you to customize the surface area to fit the user’s trunk. This will increase the pressure distribution.
Shape
Pressure distribution and trunk stability are the objectives, so choosing a pad shaped to fit the body’s anatomical curves will increase pressure distribution more than a normal square pad.
Size
Size of the pad has to be considered especially if you don’t want to impinge movement of the arms and shoulders. A small pad, when placed in the right positions to fit curvature, can provide stability and balance to even to heavy leaders.
2. Hardware
When selecting wheelchair lateral trunk support, one has to consider if the user will need to be able to remove it independently during transfers or if he/she will need the support of a caregiver.
Consider if the hardware will allow you to adjust where the swing away latch is placed according to the user’s needs.
And also consider if the hardware allows for angling of the pad, and how close it allows you to get into the trunk.
Conclusion
There are limitations to using a wheelchair lateral trunk support, as there is with any product out there, but the benefits outweigh the downsides.
The healthcare professional work together with the wheelchair professional and therapist among others to provide the best care to patients and recommending choice lateral trunk supports for them.
The objectives remain the same: minimize pain, correct deformity or prevent further deformity, provide comfort, prevent pressure ulcers, and improving functionality and safety.
Tip: Here’s our Guide to Pressure Ulcer Prevention Products.


















0 Comments