In this article, we will be exploring everything you need to know about Supplements for Degenerative Disc Disease in the Spine, and the best supplements for the diseases from the all.
Over 40% of individuals under the age of 30, and 90% of individuals above 50 years of age are diagnosed with degenerative disc disease. While there is yet to be found an effective non-invasive cure to stop the progression of the disease, there are many treatment options which can address the symptoms. Many of these treatments may require a change in lifestyles, such as quitting cigarettes, change in nutrition and diet. But following a strict diet may be difficult and demanding, which is why sometimes supplements are needed.
It is important to know which supplement is right for you, when to take supplements, the benefits and side effects of these supplements. In knowing these non-surgical treatment options, you can start your journey towards living with degenerative disc disease.
Before jumping into the supplements, let’s find out what the degenerative diseases really are.
What are Degeneration Disc Diseases of Spine?
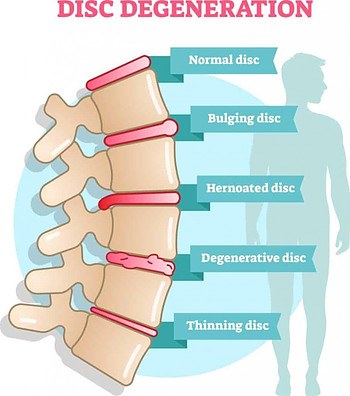
Degenerative Disc Disease, also Spondylosis, is the gradual deterioration and breakdown of one or more intervertebral disc in the spine, that causes symptoms of pain. It often leads to other complications in the spine such as arthritis, sciatica or herniated disc too.
Intervertebral discs or Spinal discs are tough, fibrous structures that behave like ligaments between vertebral bones, providing cushioning while absorbing pressure in the spinal column. Spinal discs are sturdy yet flexible, allowing the back to twist and bend.
As an individual progresses in age, these discs which act as a shock absorber begins to wear out and breakdown.
Degenerative disc disease comes naturally with age, and is better known as a natural development instead of a disease. Though there have been exceptions where individuals as young as 21 have this condition, some even inherit a prematurely aging spine.
Symptoms of Degenerative Disc Disease
Symptoms of the degenerative disc disease range from mild to severe pain in the neck (cervical) or lower back (lumbar) regions of the spine. These regions are frequently in use which accelerates the aging process and degeneration of the spinal disc.
In most cases, the early stages of degenerative disc disease are characterized by pain, stiffness and discomfort. But when it progresses to later stages, the spine gradually stabilizes, and the pain grows less to none.
-
Upper back and Neck (cervical) Degenerative Disc Disease
Cervical disc degeneration develops when one or more of the spinal discs in the cervical spine starts to deteriorate due to wear and tear.
Usually, there are 6 gel-like cervical discs, one in between every cervical spine’s vertebrae. As the neck moves, cervical discs absorb shock and prevent the vertebral bones from rubbing against each other.
-
Lower back (lumbar) Degenerative Disc Disease
Lumbar degenerative disc disease is when damaged spinal discs in the lumbar spine which causes pain in the lower back
due to wear and tear.
Causes of Degenerative Disc Disease Pains
Spinal discs have very little innervation, and so a degenerative spinal disc will rarely lead to pains or other symptoms. What usually causes pain, however, is when the degenerating disc affects other spinal structures such as joints, muscles, or nerve roots.
Degenerative disc disease pain is mainly caused by 2 things.
1. Abnormal tiny movements
Naturally, the support and cushioning a disc provides reduce as the disc degenerates leading to little abnormal motions between vertebrae.
These tiny movements can cause irritation and tension in the surrounding joints, muscles and sometimes nerve roots. Gradually, the spinal segment will become more unstable, causing periodic episodes of increased severe pain.
2. Inflammation
As the disc degenerates, inflammatory proteins from the disc can spread to surrounding spinal structures, causing them to swell. The inflammation can generate muscle spasms, muscle tension and local tenderness in the neck or back.
If it spreads even unto nerve roots and they become inflamed, the pain and numbness may radiate into the hips or legs (for a lumbar disc degeneration), or into the arm and shoulder (for a cervical disc degeneration).
Why Do the Spinal Discs Continue to Degenerate?
Blood vessels and nerve roots can only penetrate the outermost parts of the discs, and this means they have little innervation and restorative ability. Most of the nutrition discs receive is by means of the distribution of blood cells through the endplates.
Discs are made of three parts, the tough flexible exterior, a soft cushioning interior, and the cartilaginous endplates connecting the discs to the vertebrae.
Degenerative discs are characterized by significant dehydration (the soft interior is a mixture of protein and water); making the disc smaller, stiff and prone to tear at the exterior.
It’s important to understand the non-degenerative disc diseases to understand the degenerative diseases better.
Tip: Our previous articles explain disc prolapse, disc protrusion and disc bulging in more detail.
What are the Common Non-degenerative Diseases of the Spine?
Non-degenerative diseases of the spine can be categorized into a few categories.
1. Infections and Inflammatory diseases
They include the following diseases.
- Pyogenic disc space infection (diskitis)
This is commonly caused by genital and urinary infections such as staphylococcus and streptococcus, or following recent spinal surgery.
- Vertebral osteomyelitis
- Granulomatous infection
The most common types of infections in the spine are fungal infections, tuberculosis, and brucellosis.
- Epidural abscess
This is commonly caused by staphylococcus aureus, in fact in 45% of the time. Individuals with this infection usually have a history of urinary tract infection, intravenous drug abuse, recent surgery, immunosuppression or heart infection.
- Meningitis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Transverse myelitis
- Subacute combined degeneration
This is the most common cause of vitamin B12 deficiency in America, because it affects the terminal ileum.
It also affects the cervical and thoracic spinal cord and can cause lesions in the brain, optic tracts and peripheral nerves.

Tip: some nerve damages are unexplainable.
2. Cystic lesions of the cord
- Syringomyelia
- Tumor.
Cysts are commonly associated with neoplasms in the spinal cord, and are termed tumoral or non-tumoral.
3. Neoplastic diseases involving the spine and spinal cord
- Intramedullary lesions
- Ependymoma
It is the most common primary cause of spinal tumors. They are responsible for 50-60% of spinal tumors in mostly male adults between 30-50 yrs.
- Astrocytoma
About 40% of spinal tumors involve these neoplasms. They are the second most common primary cause of spinal tumors, in children and adults in their middle ages.
- Hemangioblastoma
This vascular lesion is the third most common primary cause of spinal tumors.

4. Spinal cord trauma
Many of these non-degenerative diseases can regress and disappear with treatment, if they’re discovered and treated early.
When Should You Take Supplements to Strengthen Spine?
Supplements are just that, supplements. They are used to fill in gaps in a person’s nutrition, and should be taken when there’s a nutrient deficiency in the body system.
Your spinal bones and your whole body can stay strong when it is fed with nutrients such as minerals and vitamins. These nutrients are found in a balanced diet, but when medical issues or inadequate diet causes a nutritional gap, supplements can then be used to fill those gaps.
Individuals with degenerative disc disease are often found to be deficient in certain minerals and vitamins. And this deficiency often increases the degeneration of the spinal discs.
The right supplements, whether minerals, dietary or vitamins, when taken over time can stop (least slow down) the degeneration process and improve the overall spinal health.
How to Know Which Supplement is Right for You?
Supplements have a lot of benefits, but can also be dangerous.
For example, some supplements interact with other drugs like blood-thinning medications and may increase the risk of bleeding. It is therefore important you talk to your medical doctor based on your medical history, before taking any supplement.
When Should You Not Take Supplement to Strengthen Spine?
If you are generally healthy, has an active lifestyle and get enough nutrients from food sources, you may not need supplements.
The amount of nutrient you will need from a supplement is dependent on the amount of nutrition you get from food. As long as you get the daily amount of nutrition recommended from food there’s no need to supplement or fill any gap.
It is important to know that taking supplements that you don’t need has no added benefits, but may even pose some risks.
What are the Vitamins That Can Improve Spine Health?
1. Vitamin B
B vitamins come with individual benefits and functions for general well being, but more specifically, vitamin B6 and B12 contribute to spine health.
These vitamins are best gotten from natural food sources, but if an individual has a deficiency then a supplement can be used to correct it.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 (also pyridoxine) is involved in the creation of neurotransmitters, amino acid metabolism and production of red blood cells.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 (also cobalamin) has to do with DNA and red blood cells production, as well as neurological function.
Sources of vitamins B6 and B12
- Food
Natural sources like dairy, meat, seafood, and eggs are rich in vitamin B12.
Potatoes, chickpeas and salmon are all high in vitamin B6.
- Supplements
You may require supplements to meet your nutritional needs.
Before taking B-Complex supplements, get a recommendation from your doctor based on your medical history and nutritional needs.
It is important to choose B-Complex supplements from reputable brands tested by the USP (US Pharmacopoeia Convention).
[et_bloom_locked optin_id=optin_3][/et_bloom_locked]
2. Vitamin D
Vitamin D mainly helps the body to absorb calcium, which the kidneys would otherwise expel. Without adequate vitamin D, the bones can become unhealthy, brittle or thin.
Over 80% of people in the United States do not have enough vitamin D in their body.
Cases of degenerative disc disease have also been associated with Vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble hormone and not actually a vitamin, which the skin produces in response to sunlight.
Vitamins cannot be created by the body; they have to be consumed in a diet. However, Vitamin D can be produced by the body and can also be obtained from a diet.
Sources of vitamin D
Unlike most of the other vitamins, vitamin D has 3 potential sources.
- Food
Food sources of vitamin D not limited to fatty fish such as tuna, wild-caught mackerel, and salmon.
Very few foods contain vitamin D, but they can also be found in dairy products, milk, fortified cereals, orange juice, and soymilk.
- Sunlight
Our bodies can produce vitamin D in reaction to sunlight and store it as fat to be used later. But our bodies may not produce enough vitamin D from sunlight because of factors like the pigmentation of the skin, time of the day, age, your latitude, season and other factors.
Some other factors, like people who stay mostly indoors, and people who use sunscreen when outdoors to prevent skin cancer, also reduces the amount of vitamin D the body will produce.
- Supplements
Since it is difficult to get adequate vitamin D from food sources alone, some people have to take supplements to support bone and spine health.
Vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are the two types of vitamin D, and they’re both good for bone health.
Before taking a vitamin D supplement, find out if your other medications, multivitamins, or supplements contain vitamin D.
Vitamin D supplements can be taken together with of foot or with no food.
It is good to note that, even though vitamin D helps with the absorption of calcium, they are not to be taken together or at the same time.
And, as noted above, be sure to consult with your doctor or pharmacist for any recommendations.
3. Other vitamins
There are several other vitamins that are essential for healthy connective tissues and bones such as Vitamins A, C, E, K.

What Minerals That Can Improve Spine Health?
1. Calcium
Calcium is an essential mineral in everyday living. Apart from contributing greatly to bone health, it comes with other benefits such as assisting in blood clotting, heartbeat and muscle contraction.
Our bones and teeth contain about 99% of the calcium in the body, and our bodies are unable to produce their own calcium. Every day our bodies lose calcium through nails, skin, hair, urine, sweat and feces. So, you can see why it is important to get enough calcium from the food we consume, or supplement to make up for it.
When our body doesn’t have the required amount of calcium it needs to function daily, it can lead to low density in bones, bone loss and even broken bones.
Sources of calcium
There are 2 sources of calcium; food and supplements.
- Food
Food sources such as dairy products (yogurt, milk, cheese) are rich in calcium, some green vegetables also contain calcium.
Cereals, soymilk, breakfast foods, bread, snacks, some orange juices, and even (some) bottle water contains added calcium.
- Supplements
There are various calcium supplements available without a prescription, both in liquid and chewable preparations.
Tips on Choosing a Calcium Supplement
Here are some tips for choosing and taking a calcium supplement:
- Most calcium supplements are taken with food, except for calcium citrate, which can be taken with or without food.
- In choosing calcium supplements, go for reliable brand-name supplements. Look for labels that have the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) symbol, or the ones that state ‘purified’.
- Calcium supplements should be taken in doses of about 500-600 mg 2-3 times a day, and not higher than that.
- If you’re switching to a new calcium supplement, it is better to start small (between 200-300 mg) for better tolerance. Then gradually go higher each week with plenty of water.
- Calcium supplements shouldn’t be taken with a laxative or high fiber food, to avoid interference.
2. Other minerals
Minerals such as magnesium, copper, boron, zinc, and manganese are also vital for healthy bones and connective tissues.
Now, let’s turn into herbs.
[et_bloom_locked optin_id=optin_3][/et_bloom_locked]
What are the Herbs That Can Improve Spine Health?
These herbal remedies can help treat degenerative disc disease symptoms, relief back pains and improve spine health. It may come in the form of tea; capsules, pills or tablets; liquid/tinctures extract.
-
Capsaicin cream
It is applied to the skin in the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain.
-
White Willow bark
Willow bark is used as a pain reliever, but it interacts with blood-thinning medications and aspirin, so taking them together is not advised.
This herb should not be given to children under the age of 18 or individuals allergic to salicylate or aspirin.
-
Devil’s claw
Devil’s claw reduces pain. Although it may affect people with gallstones, and can also affect the heart.
Remember, it interacts with diabetes medication and may increase the risk of bleeding.
-
Tumeric
Turmeric reduces inflammation and relieves pain. But for people taking blood-thinning medications, it may increase the risk of bleeding.
Tip: Some back pains can heal on its own with the help of a patch such as ActiPatch.
Nutritional Tips for Better Spine Health
1. Eating right
Reducing the amount of sugar you consume should be the first step.
Each year the average American consumes about 100 lbs of sugar. High sugar diets are high in Omega 6 fatty acids which elevates inflammation.
In eating wisely, you can give your body an extra boost of healing power.
Some superfoods that boost the healing of your spine include:
- Red fruits and vegetables
Fresh or stewed tomatoes, beet, red pepper, dark berries such as blackberry and blueberry.
- Beans
Soybeans, navy beans etc.
- Shellfish
Oysters, crab, shrimp etc.
- Coldwater oily fishes
Mackerel, salmon, sardines etc.
- Dark green vegetables
Asparagus, spinach, kale etc.
- Olive oil
- Black olives
- Seeds
Chia seeds, flax seeds
- Red onions
- Fruits
Especially apples.
- Grains
- Nuts
- Other vegetables
- Winter squash
2. Exercise/Yoga
Detoxify your body of stress and stress hormones with simple yoga, meditation and massage. Exercising with the help of a coach, or physical therapy expert, will help to relieve degenerative disc disease pains as well.
Light exercises strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, aids increased blood flow to the spine, and keeps body weight in check.

Tip: Sensation of muscle pains are not the same as nerve pains.
3. Staying hydrated
More than 70% of the human body is made of water, and 80% of the spinal disc is also made of water.
Water is essential in the repair, growth and function of all avascular white tissues, which includes the spinal discs, ligaments, joints and cartilages.
A person’s daily water intake should be an ounce of water per 2 pounds of your body weight. That means if you weigh 200 lbs then you should take 100 ounces of water a day.
Most individuals with degenerative disc disease are already dehydrated.
4. Supplements
Make sure you have enough of the below essentials, and if not consider supplements.
- Omega 3 fatty acid
- Bromelain
- Chondroitin, and
- Glucosamine
5. Things to avoid
Trying to live healthy by taking supplements to boost your spine health does not make sense if you have the below unhealthy habits.
- Cigarette smoking, alcohol addiction, or coffee addiction
They can all obstruct the healing process.
- Unhealthy eating
Foods are high in trans-fat, saturated fat and sugar such as fast food, cookies, cake, dessert.
Processed foods like hot dogs, lunch meats and sausage, are high in nitrates.
Foods containing high fructose corn syrup.
[et_bloom_locked optin_id=optin_3][/et_bloom_locked]
What Research Say? And, Cautions!
Is there a cure for degenerative disc disease? Many research and studies have been conducted in an effort to get a permanent treatment for degenerative disc disease. And many have only succeeded in developing treatments for the symptoms and not really a cure that addresses the cause of the degeneration in a non-invasive way.
But in recent times, there have been some promising results.
About six years ago, Prof. Keita Ito and his group at the Eindhoven University of Technology first started the research on injectable cell-derived Matrix. The new Biomaterial currently being developed by NC Biomatrix, is a cell-derived matrix gel that can be injected into the spinal disc directly.
The aim of NC Biomatrix, according to its CEO Robert Guilleaume, is to develop an injectable, non-invasive treatment to degenerative disc disease, that would restore the interior of the spinal disc to its original height and volume as before degeneration. Their experiments showed that the cell-derived matrix gel also acts as a platform that causes the cells in the disc to produce the proteins needed to reverse the degenerative process. Although, this isn’t 100% proven yet.
Note, however, that there’s currently no cure for degenerative disc disease; it can only be managed by treating the symptoms of pain.
When to Seek Medical Help?
When the pain from degenerative disc disease with associated spinal degenerations becomes severe, you must seek help to avoid the unavoidable.
And, pain medications, physical therapy as well as non-surgical treatments, prove ineffective, then surgery is recommended to address the symptoms — all with doctor’s recommendation.
Before surgery is recommended, non-surgical treatments are suggested for 6-12 weeks or longer. Only about 30% of cervical disc degeneration cases and about 10-20% of lumbar disc degeneration cases are unresolved using non-surgical treatments and require surgery to improve mobility and relieve pain.
What are the Surgeries of Degenerative Disc Disease?
There are two types of surgeries currently available for degenerative disc disease.
-
Lumbar fusion surgery
Spinal fusion surgery halts the movement at a painful vertebral segment. By replacing a mobile joint with a bone graft in a segment of the spine, the accompanying boney fusion halts the movement at that joint segment. This should reduce the pain generated from the joint.
-
Artificial disc replacement surgery
This surgery aims at mimicking the function and form of a natural spinal disc. The painful degenerated disc is replaced with an artificial disc.
Things to Consider Before Undergoing Spine Surgery
It is important to consider the drawbacks, potential risks and other factors involved before surgery. Every non-surgical treatment option should be exhausted to the patient’s satisfaction before opting for surgery.
- The outcome is not always predictable.
There’s a possibility that even after surgery and recovery, the pain might still remain. Although in most cases the pain is successfully alleviated.
- The recovery process after spinal surgery can consist of pain medications, physical therapy, wearing a neck or back brace, or a combination of all of them.
- It will require a change in the everyday lifestyle of adjusting to physical therapy, pain medications and so on. Also, it may require staying off work for a long while, depending on the recovery period.

Tip: Can you believe knee pillows such as ComfiLife can help you manage back pains?
Conclusion
Although degenerative disc disease is very common, it can still be prevented or managed through; the healthy lifestyle of no smoking, no alcohol, and less sugar.
Secondly, eating a well-balanced diet with the right vitamins
and minerals. If it seems difficult to attain, then go for the right supplements to support your immune system and keep you healthy.
Thirdly, exercising and keeping fit is also important. A healthy back and a healthy weight is the key. Always refer to your healthcare professional when you get ‘confused’ and need advice.






0 Comments