Have a pain in the right lower abdomen radiating to your groin or navel? Chances are you may be experiencing acute or chronic appendicitis related groin pain. While this is a very common scenario as most people would come across during their lifetime, especially at young ages, there are ways you can avoid such infections of appendix requiring surgery. In this article, we will be exploring the Medically Recommended Lifestyle to Avoid Appendicitis. Mainly, the lifestyle before appendicitis, which would potentially prevent it. And then, the recommended lifestyle after undergoing surgery for appendicitis.
Before diving into the lifestyle recommendations, let’s learn a bit more acute appendicitis.
What is Acute Appendicitis?
You may be aware of the body organ called ‘Appendix’ located at nearly at the end of the digestive tract, closer to the junction of the small intestine and large intestine. It is a finger-shaped pouch that hanging from your colon on the lower right side of your abdomen.
It seems to be very small in size but once infiltrated with bacterial infection can cause substantial health problems, indeed. Moreover, the sickness caused by bacterial infection once infused into the appendix is known as appendicitis.
The appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix that can cause fever, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and as a result, can elevate off the neutrophil count in the blood.
Acute appendicitis is defined as a severe irritation to the above mentioned vermiform appendix, most likely caused by a blocking of the lumen of the appendix by normal stool, infective agents, or as a result of the condition called lymphoid hyperplasia, respectively.
Furthermore, as research also sometimes suggest the sole symptom that you experience appendicitis is an ache in your lower right abdomen area. However, clinical practice suggests in most people, this pain begins around their navel and then moves downwards.
As the irritation worsens, appendicitis ache typically will increase and sooner or later becomes severe.
Although any person can boost appendicitis, most often it occurs in the young, the people between the age ranging from 10 to 30.
A clinical diagnosis of appendicitis is important. If an investigation is required, CT scan or Ultrasound may also be used to confirm expansion to the appendix’s outer diameter to be over 6 mm.
The ultimate solution and the standard treatment is the surgical elimination of the appendix by a surgical procedure called ‘appendectomy’.
How Common is the Appendicitis?
Around 40,000 people are diagnosed with appendicitis every year in the UK. Appendicitis can develop at any stage of your life, but as I mentioned earlier, it occurs most commonly within young people at the age of 10 to 20 years old. Neglecting in paying attention to appendicitis can be life-threatening.
Appendicitis is considered the second most common acute inflammatory condition among children. In children, the diagnosis of appendicitis is extremely difficult because over 40% of the infected patients show very peculiar symptoms. As such, complicated appendicitis, which is referred to as ‘perforated appendicitis’, is a commoner circumstance in children than in adults.
Appendicitis is uncommon in the case of the older people, but given the symptoms are usually very mild at the initial stages, in most cases the diagnosis delayed and treatment are not quickly initiated. People of this age are thus at the higher risk of damage from the bursting of infecting appendicitis, which is a serious medical emergency.
Appendicitis is usually diagnosed with physical observation and patient history. Several different techniques are helpful in the diagnosis of appendicitis, such as white blood cells count, urinalysis, CT scan, laparoscopy, and ultrasonography. We will discuss the diagnosis a bit later in this article.
Appendicitis is not an inherited disease and is not transmitted from person to person. But, what causes it? Let’s find out.
Tip: If you are with diabetes, best to stick with Chinen salt instead of regular salts.
What are the Causes of Acute Appendicitis?
Acute appendicitis is generally induced by way of a bacterial infection, although the cause the appendix turns into contaminated if not deduced correctly. Moreover, in some instances, it is observed that the appendix might appear as obstructed by using a lump of feces, fecal debris, and calcium salts or tumors, that can lead to infection. Besides, swelling and inflammation pave the path for infection, blood clot, or rupture of the appendix, respectively. However, the scientists believe if you are with any of the below conditions, that’s as a risk factor to experience appendicitis. That’s because they are associated with the condition lymphoid hyperplasia of the appendix, which also can result in appendicitis.
- Crohn disease
- measles
- gastroenteritis
- amebiasis
- mononucleosis
- respiratory infections

Tip: Remember, inflammation could affect your blood pressure.
What are the Common Symptoms?
The common signs and symptoms of acute appendicitis might also be deceptive; however, if you experience the conditions mentioned below, there is a chance of a ‘bad news’ so seek your doctor’s appointment immediately.
- Vague pain or tenderness close to the navel (early in an attack), migrating to the proper lower quadrant of the abdomen.
- The sudden ache that starts evolved around your navel and regularly shifts to your lower proper abdomen.
- Sharp, localized, continual pain inside a few hours.
- Pain that can worsen with movement, deep breathing, coughing, and sneezing, on foot or if it’s touched.
- Constipation and lack of ability to skip gas, possibly alternating with diarrhea.
- An excessive fever (possibly accompanied by using chills) may additionally indicate an abscessed appendix.
- Increase in a heartbeat that causes disturbances.
- Abdominal swelling in late stages.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- The tongue can get white coating and awful breath.
- Painful urination.
- Blood in the urine.
- There can be Swelling or bloating in the abdomen, particularly in infants.
- If you are pregnant, the pain may appear to come from your higher abdomen due to the fact your appendix is greater for the duration of pregnancy.
What is Chronic Appendicitis?
How to Diagnose Appendicitis?
These are ways to diagnose appendicitis.
- In addition to the physical examination is ruled out because different problems produce signs comparable to those of appendicitis.
- A rectal examination is recommended for the diagnosis of appendicitis.
- For analysis, blood and urine samples are also taken.
- CT (computed tomography) scan or a stomach x-ray may be necessary.
- Diagnosis is based on the physical examination and the condition of the patient. But several different techniques are helpful in the diagnosis such as white blood cell count, ultrasonography.

Detail of some key techniques is given below:
White blood cells count
As there is no specific test or technology for diagnosing appendicitis (or infection in the appendix), complete white blood cells are counted to check the condition of infection anywhere in the body.
Approximately 90% of the people with acute appendicitis generally have an increase in the number of white blood cells (WBC). The sensitivity and the specificity of the WBC are very low, so it is not considered as a good indicator of appendicitis (but an infection anywhere in the body).
Urinalysis
Urinalysis generally does not show infection, but it is important in the diagnosis of the urinary tract infection and to know whether urinary tract infection is the cause of the abdominal pain or not. This is to exclude urinary tract infection, as the symptoms of both conditions greatly overlap.
CT scan
CT scan is the most preferable for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in adolescents and young people.
The sensitivity and the specificity of the CT scan are much higher in the case of the appendicitis diagnosis as compared to the Ultrasound. Ultrasound is also effective in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis but in the case of the children and young adults, not.
X-rays
Plain abdominal radiographs or X-ray films are useful for the diagnosis of the fecal obstruction, calcified salt blockage and the blockage of the vessels.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is most commonly used in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis these days, especially in the children and in pregnant females. During pregnancy, it is most useful during the second and the third trimester because the appendix is pushed towards the side by the enlarging uterus. This makes it challenging to locate and assess the appendix in those individuals, so the help of this more advanced technique needed.
How to Treat Acute Appendicitis?
You should call your health practitioner immediately.
Still, if you are doubtful of your symptoms, take your temperature every two hours and keep a record for your doctor. Appendicitis cure generally involves a surgical procedure to put off the inflamed appendix, which is considered a ‘simple day surgery’.
Before undergoing the surgical procedure though, you are most likely prescribed to take a dose of antibiotics to deal with an infection. The appendix ought to be eliminated either by an appendectomy,
through a small incision or with a distinct instrument ‘laparoscope’.
Depending on the severity of your appendix infection, you should not make any delays to the surgery but should stick with your doctors (i.e. surgeon) recommendations. If an abscess has formed, your doctor might also drain it and prescribe antibiotics. Appendectomy might also be scheduled for a later date as well, again depending on your individual circumstances.
Appendectomy: A Surgery to Remove the Appendix
Indeed, the surgical procedure, commonly known as ‘appendectomy’ can be performed as open surgery. This involves one abdominal incision, which is about 2-4 inches (5 to 10 centimeters) to get access to your abdominal cavity(laparotomy).
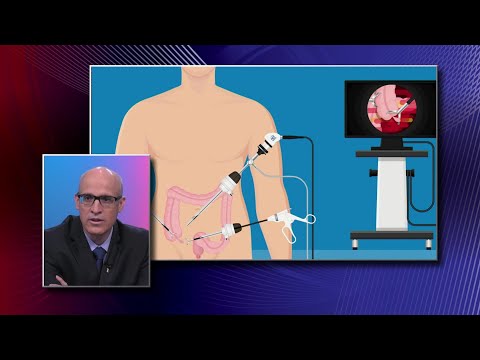
Or, instead, the surgical procedure can be completed via a 3 to 4 small abdominal holes, which is referred to as keyhole surgery or laparoscopic surgery. During a laparoscopic appendectomy procedure, the surgeon inserts surgical tools and a video camera into your abdomen through the keyholes, and remove your appendix. This occurs by looking into the video image from the camera.
In general, the laparoscopic surgical operation allows you to get better quicker and heal with much less ache and scarring. It might also be better for older adults and people with overweight and obesity.
But the laparoscopic surgical procedure is not fabulous for everyone. In particular, a case when your appendix has ruptured, when the infection has spread beyond the appendix, or you have an abscess or gangrene at the appendix, you are not suitable to undergo keyhole surgery but an open appendectomy, which allows your doctor to smooth the belly cavity.
Now, with all the above knowledge about acute and chronic appendicitis, let’s turn our attention to the most important topic of this article ‘the Recommended Lifestyle to Avoid Appendicitis’.
How to Prevent Appendicitis?
Unfortunately, observation shows that there is no definitive preventive measure to avoid appendicitis. On the contrary, to popular belief, swallowing seeds from fruit does not precipitate appendicitis is just a myth.
But, there is a recommended lifestyle you can stick with which could help you avoid infection following surgery.
Recommended Lifestyle to Avoid Appendicitis is simple as a ‘healthy lifestyle’ as we all know of.
So, What Kind of Lifestyle and Domestic Remedies Should You Adopt? Let’s find out.

How to Recover from Surgery?
Expect a few weeks of recuperation from the surgery appendectomy, or longer specially if the appendix did end up with a burst before surgery. To help your physique heal; you should follow a proper set of habits such as the below.
-
Avoid strenuous activities for at least weeks to months.
If you have undergone an appendectomy, restrict your recreation for at least 3 to 5 days. Especially, if the surgery was an open appendectomy, you should avoid any physical stress on your body for at least 10 to 14 days.
Again, as mentioned earlier, always ask your doctor about what you can do, can’t do and limit endeavour. The doctor should also have a better idea of when you can resume everyday things you do, after surgery.
-
Support your stomach when you cough.
Place a pillow over your stomach and observe stress earlier than you cough or laugh. Remember, cough and laugh could cause pain and ‘stress’; the surgical site wound is currently healing.
Tip: Here’s our Knee Pillow Guide for back and side sleepers.
-
Get advice!
Call your health practitioner if your medicinal pain drugs are not helping you. Remember, for some people undergoing surgery and then resting during the recovery can put more significant stress on your physique and slow down the recovery. Regardless, if you are still in pain in spite of the pain killers, your doctor prescribes you to take, call your doctor for a review.
-
Get up and cross only when you are ready.
You underwent surgery, and body is healing now at its pace. Be kind to yourself and start slowly and then increase your pastime towards your regular lifestyle slowly. Start with quick short walks before thinking about a marathon or your ‘stressful’ job.
-
Sleep when tired.
As your physique heals, you may notice that now you feel sleepier and tired than how it’s used to be. It is equally important to take it easy, relax your self and rest when you need it the most.
-
Discuss returning to work with your doctor.
You can return to your regular employment when you feel up to it, usually after a week or two. Children should be in a position to return to school, in most cases, within a week after surgery. Again, this does not mean that you can return to your full lifestyle including any strenuous activities you used to do soon after 2 to 4 weeks from surgery. Your healing body will guide you, but the idea is not to push its healing process from the surgery.

Conclusion
In a nutshell, we say that although the appendix is a vestigial organ with no regarded function, it can end up diseased fatally.
Acute appendicitis is one of the most frequent motives for stomach surgical operation in the world. Therefore, it is advised to keep in mind all the prescribed symptoms and if you find any particular consistent sign for longer periods, then without a doubt, get a medical diagnosis from your health practitioner respectively.
Stay safe and healthy and enjoy a vigorous life with your loved ones by taking care of your health during and after surgery. And, there is no way you can plan and prevent acute and chronic appendicitis.




0 Comments